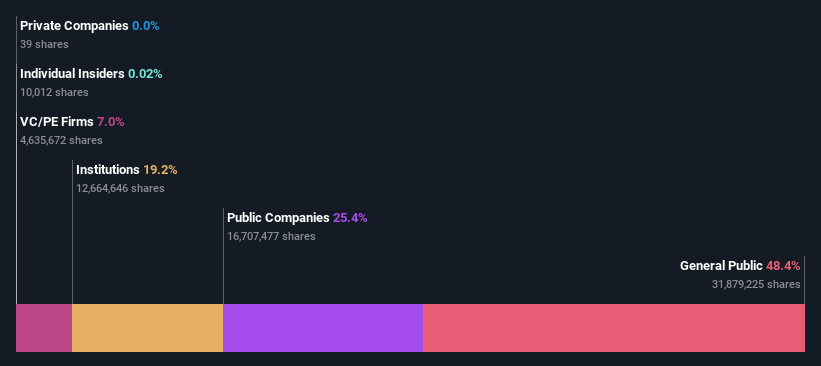
Retail investors are Galapagos NV's (AMS:GLPG) biggest owners and were hit after market cap dropped €74m
Key Insights
Significant control over Galapagos by retail investors implies that the general public has more power to influence management and governance-related decisions
The top 13 shareholders own 50% of the company
To get a sense of who is truly in control of Galapagos NV (AMS:GLPG), it is important to understand the ownership structure of the business. The group holding the most number of shares in the company, around 48% to be precise, is retail investors. Put another way, the group faces the maximum upside potential (or downside risk).
And following last week's 4.5% decline in share price, retail investors suffered the most losses.
Let's take a closer look to see what the different types of shareholders can tell us about Galapagos.
View our latest analysis for Galapagos
What Does The Institutional Ownership Tell Us About Galapagos?
Institutions typically measure themselves against a benchmark when reporting to their own investors, so they often become more enthusiastic about a stock once it's included in a major index. We would expect most companies to have some institutions on the register, especially if they are growing.
We can see that Galapagos does have institutional investors; and they hold a good portion of the company's stock. This implies the analysts working for those institutions have looked at the stock and they like it. But just like anyone else, they could be wrong. If multiple institutions change their view on a stock at the same time, you could see the share price drop fast. It's therefore worth looking at Galapagos' earnings history below. Of course, the future is what really matters.
Hedge funds don't have many shares in Galapagos. Looking at our data, we can see that the largest shareholder is Gilead Sciences, Inc. with 25% of shares outstanding. Van Herk Investments B.V. is the second largest shareholder owning 7.0% of common stock, and FMR LLC holds about 6.2% of the company stock.
A closer look at our ownership figures suggests that the top 13 shareholders have a combined ownership of 50% implying that no single shareholder has a majority.
Researching institutional ownership is a good way to gauge and filter a stock's expected performance. The same can be achieved by studying analyst sentiments. Quite a few analysts cover the stock, so you could look into forecast growth quite easily.
Insider Ownership Of Galapagos
The definition of company insiders can be subjective and does vary between jurisdictions. Our data reflects individual insiders, capturing board members at the very least. The company management answer to the board and the latter should represent the interests of shareholders. Notably, sometimes top-level managers are on the board themselves.
Most consider insider ownership a positive because it can indicate the board is well aligned with other shareholders. However, on some occasions too much power is concentrated within this group.
Our most recent data indicates that insiders own less than 1% of Galapagos NV. It's a big company, so even a small proportional interest can create alignment between the board and shareholders. In this case insiders own €240k worth of shares. It is good to see board members owning shares, but it might be worth checking if those insiders have been buying.
General Public Ownership
The general public-- including retail investors -- own 48% stake in the company, and hence can't easily be ignored. While this group can't necessarily call the shots, it can certainly have a real influence on how the company is run.
Private Equity Ownership
Private equity firms hold a 7.0% stake in Galapagos. This suggests they can be influential in key policy decisions. Sometimes we see private equity stick around for the long term, but generally speaking they have a shorter investment horizon and -- as the name suggests -- don't invest in public companies much. After some time they may look to sell and redeploy capital elsewhere.
Public Company Ownership
Public companies currently own 25% of Galapagos stock. We can't be certain but it is quite possible this is a strategic stake. The businesses may be similar, or work together.
Next Steps:
It's always worth thinking about the different groups who own shares in a company. But to understand Galapagos better, we need to consider many other factors. Consider for instance, the ever-present spectre of investment risk. We've identified 2 warning signs with Galapagos (at least 1 which makes us a bit uncomfortable) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
Ultimately the future is most important. You can access this free report on analyst forecasts for the company.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance