More in work will mean billions less borrowing

Employment levels in the UK have beaten the expectations of the Office for Budget Responsibility, with important implications for the state of the country’s public finances.
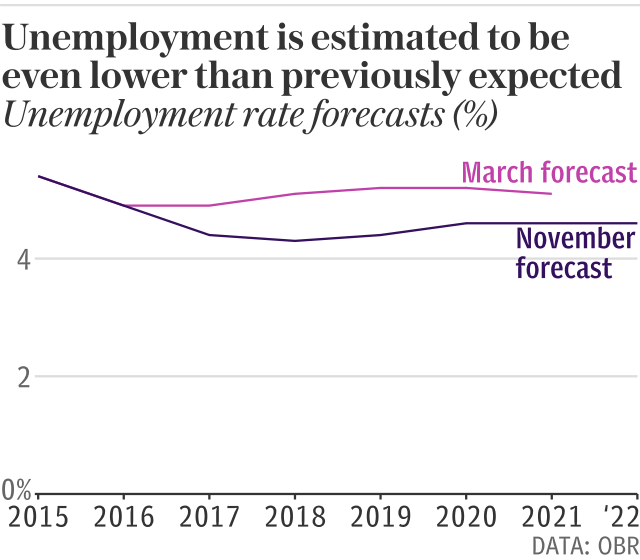
The OBR has reduced its forecast for unemployment over the next five years, after finding that it was better than it had projected in March, at 4.3pc – representing the lowest rate since 1975.
Increased employment levels will have a meaningful benefit for the public finances, according to the OBR’s calculations.
The combination of more hours being worked and a reduction in the unemployment rate will reduce public borrowing by £10.7bn by 2021-22.
Significantly, the financial watchdog also outlined an “equilibrium rate”, the level below which wages would take off and add significant pressure to inflation, as 4.5pc.
It added that rises in the National Living Wage would increase that tipping point to 4.6pc by 2021-22. The OBR also found that employment was higher and the total number of hours worked had grown at nearly twice the rate it had expected, at 0.9pc.
Robert Chote, the chairman of the OBR, said this break in the long-term trend of workers cutting down on their hours was because of the squeeze on household incomes.
“Average hours worked per person have risen since the financial crisis, but to date we have assumed that the long-standing downward trend would reassert itself over the forecast period,” Mr Chote said.
“But this has not happened yet, perhaps because people are working longer hours than they otherwise would have to cushion their incomes from the impact of weak earnings growth.”
The OBR also suggested that strong employment levels would help support consumer demand, despite weak earnings growth.
Howard Archer, chief economic adviser at EY Item Club, told The Daily Telegraph that these changes to unemployment forecasts would “partly offset the downward revisions to productivity”.
The OBR has reduced its expectations for GDP growth from 2pc to 1.5pc in 2017 and down by 0.2 percentage points from 1.6pc to 1.4pc next year.
However, a seriously weak productivity performance in the UK meant that there should be no expectation that the better-than-hoped employment figures would result in “favourable movement” on wage growth, John Hawksworth of PwC said. This comes after top policymakers at the Bank of England told the Treasury select committee on Tuesday that they were seeing “some evidence” suggesting that earnings might soon rise, including reports that firms were finding it more difficult to recruit staff.
“Employees seem more confident to be willing to move jobs for higher pay,” added Gertjan Vlieghe, who voted to raise interest rates in this month’s Monetary Policy Committee meeting.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 