Trio wins Nobel Chemistry Prize for DNA repair work
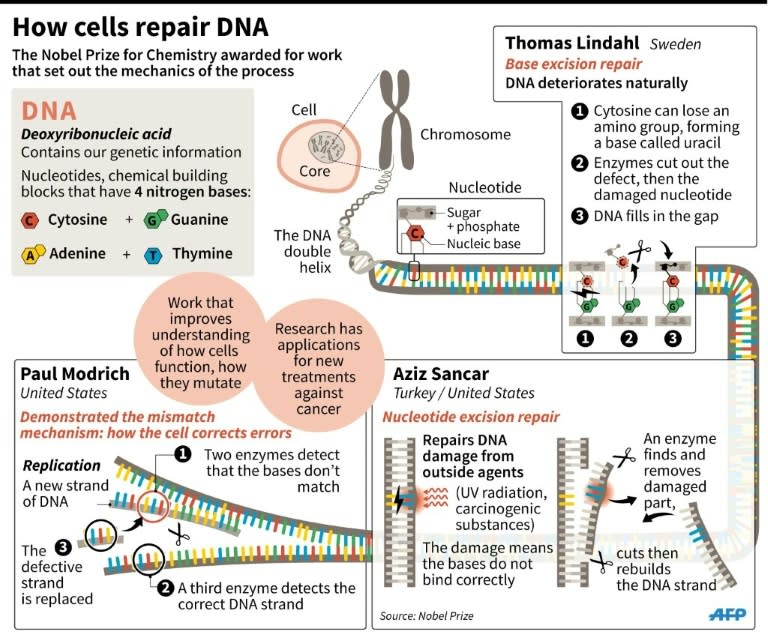
Sweden's Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich of the United States and Aziz Sancar, a Turkish-American, won the 2015 Nobel Chemistry Prize on Wednesday for work on how cells repair damaged DNA. The three opened a dazzling frontier in medicine by unveiling how the body repairs DNA mutations that can cause sickness and contribute to ageing, the Nobel jury said. "Their systematic work has made a decisive contribution to the understanding of how the living cell functions, as well as providing knowledge about the molecular causes of several hereditary diseases and about mechanisms behind both cancer development and ageing," the panel said. DNA -- deoxyribonucleic acid -- is the chemical code for making and sustaining life. Cells divide, or replicate, billions of times through our lifetime. Molecular machines seek to copy the code perfectly, but random slipups in their work can cause the daughter cells to die or malfunction. DNA can also be damaged by strong sunlight and other environmental factors. But there is a swarm of proteins -- a molecular repair kit -- designed to monitor the process. It proof-reads the code and repairs damage. The three were lauded for mapping these processes, starting with Lindahl, who identified so-called repair enzymes -- the basics in the toolbox. Sancar discovered the mechanisms used by cells to fix damage by ultraviolet radiation. Modrich laid bare a complex DNA-mending process called mismatch repair. - Lifesaving treatments - "The basic research carried out by the 2015 Nobel laureates in chemistry has not only deepened our knowledge of how we function, but could also lead to the development of lifesaving treatments," the Nobel committee said. With cells able to repair themselves, one could ponder the dizzying possibility that humans could go on living forever. "No, I don't believe in eternal life," Lindahl, who is based in Britain, told reporters by telephone at the prize announcement. He said scientists were increasingly turning their attention away from curing diseases such as cancer and instead looking for chronic treatments. "We are getting away a little bit (from) trying to find a cure for everything, and convert diseases to something we can live with," he said. DNA repair researcher Nora Goosen of the University of Leiden in the Netherlands told AFP scientists were looking at targeted attacks on cancer. She said the same mechanism by which cells repair DNA damage can also make them resist the effects of chemotherapy. By understanding how the cell repair system works, doctors hope they will one day be able to instruct cancerous cells not to fight against treatment, she explained. British biochemist Sir Tim Hunt, a co-winner of the 2001 Nobel for his work on cell duplication, led the praise for his old boss Lindahl. "He's an absolute giant in the field, a great pioneer. He was one of the first people to very accurately measure how DNA decayed naturally," Hunt said at a hastily-arranged party for Lindahl at the Francis Crick Institute just outside London. - Studies over football - It is the seventh time DNA research has been honoured with a Nobel prize. The first was in 1962, for the discovery of the structure of DNA. Lindahl, Modrich and Sancar share the prize sum of eight million Swedish kronor (around $950,000 or 855,000 euros). Lindahl, 77, is the emeritus director of Cancer Research UK at Clare Hall Laboratory in Britain. Modrich was born in 1946 and grew up in a small town in northern New Mexico, which instilled in him a love of the natural world. "There was huge biological diversity around me," he said in a statement on the website of Duke University, where he is a professor of biochemistry. "Within five miles, the ecology can change dramatically -- it was very thought provoking." In 1963, his father, who was the local high school biology teacher, gave him very important advice, he recalled: "You should learn about this DNA stuff." Modrich said he was caught by surprise when the early-morning Nobel call came in. "We're on vacation in New Hampshire, so this was sort of a shock," he said. Sancar, 69, was born in the small Turkish town of Savur. He could have become a professional football player -- Turkey's national junior team courted him to become their goalkeeper -- but he chose to focus on his academic studies instead. After working as a doctor in the countryside, he resumed his biochemistry studies at the age of 27, and then went to the University of Texas in Dallas. He is now a professor of biochemistry and biochemics at University of North Carolina in the US. "This award means a great deal to me and my lab," Sancar said in a statement. "We've been working hard for many years and I think we've made significant contributions to our field." The Nobel awards week continues with the announcements for the two most closely-watched prizes: on Thursday the winner of the literature prize will be announced, followed by the peace prize on Friday. The economics prize wraps up this year's Nobel season on Monday.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance