Living wage and skills shortage push pay up at fastest rate since 2008

Workers can expect the biggest pay rises since 2008 this year as a skills shortage combined with hikes to the minimum wage force up earnings at long last.
The average private sector employer expects to give staff an extra 3.1pc this year, according to the Bank of England’s agents who survey firms across the country.
This will be the first time pay settlements have broken through the 3pc level since the financial crisis, and should mean wages outstrip prices this year.
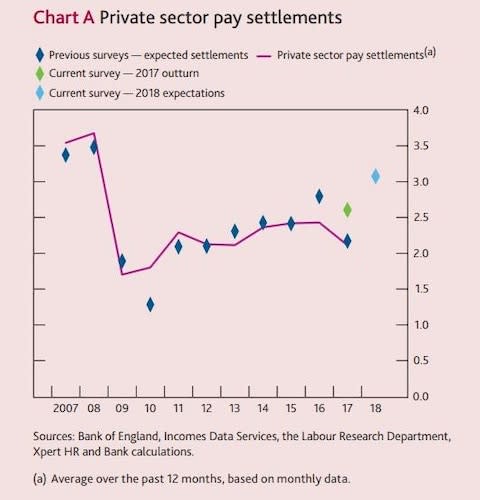
Employers raised wages by 2.6pc in 2017, faster than the 2.2pc they predicted at the start of the year and so indicating pay pressures are mounting.
Recruitment difficulties are at their highest level since 2004, firms told the Bank, with manufacturing and business services companies still keen to take on more workers.
Factories said they were bumping up against capacity constraints more severely than at any point since 2007.
The pay rises are coming across “a broad range of sectors”, the Bank’s agents said, indicating these are pressures across the economy rather than specific to any one industry. Only construction workers will not see an acceleration in earnings growth this year, as that sector is struggling more than others.
“The biggest expected increase in pay settlements is seen in consumer services. That is because many firms in this sector will have to increase pay to meet the National Living Wage (NLW),” the agents reported.
“Companies also reported an increased tendency to pay above the NLW, due to competitive pressures.”
That means more pay rises at the bottom end of the pay scale. As a result companies are looking to save money elsewhere: “Many firms were planning to limit management pay increases to 1pc–2pc in order to hold down their overall pay settlement.”

Higher inflation is also putting pressure on firms to raise wages, while other pay-related costs, including rising pension contributions, are straining employers’ finances.
These costs are feeding into further inflation as companies seek to pass on the burden.
“Consumer services price inflation had edged down, but remained under upward pressure from increases in regulated prices, such as rail fares, in addition to firms passing on higher input and labour costs,” the agents said.
This could put more pressure on the Bank's Monetary Policy Committee, headed by Mark Carney, to raise interest rates.
Wider economic activity “held steady at a modest pace”, the agents said, with investment intentions staying positive, an acceleration in the professional services market and in goods exports, but there was also a slowdown in the construction industry.
Exports are up in part because of the fall in sterling since 2016. This also benefitted British manufacturers by making their goods more competitive within the UK.
“Export volumes growth had increased, supported by strong global demand and the fall in sterling,” the agents reported.
“The latter had led to some, albeit still limited, switching from overseas to cheaper, domestically produced goods.”

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 