FOMC Preview: Powell to face 'status check' on Fed's emergency actions
The Federal Reserve is scheduled to announce its latest policy decision on Wednesday. But with rates already at near-zero, attention will likely shift to the central bank’s nine liquidity facilities and its ballooning balance sheet.
“We do not expect any major policy changes at the meeting,” Goldman Sachs wrote April 23, adding that a rate hike won’t be on the table until at least 2023.
Chairman Jerome Powell’s press conference on Wednesday afternoon could provide guidance on where it goes with its $6.6 trillion balance sheet, which grew by over $2.3 trillion since the first week of March.
For comparison, the balance sheet peaked at about $4.5 trillion following the 2008 financial crisis.
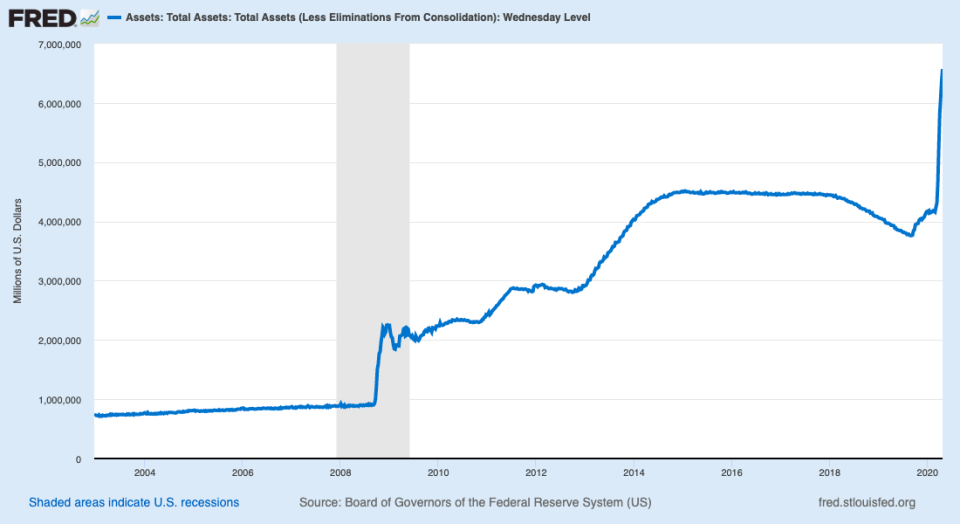
The Fed has messaged that its current purchases of Treasuries and agency mortgage-backed securities are “open-ended” - effectively a cap-less quantitative easing program.
Deutsche Bank wrote April 23 that the Wednesday decision will also serve as a “status check on the Fed’s arsenal” of tools to set the U.S. economy up for an eventual recovery.
That could include more details on the major weapons in the Fed’s arsenal: nine liquidity facilities offering a backstop to markets ranging from U.S. dollars to below-investment grade corporate debt.
Treasuries...
A majority of the Fed’s asset purchases in the COVID-19 response have been U.S. Treasuries.
Since the first week of March, the Fed has purchased about $1.4 trillion in U.S. Treasuries across the curve. The massive pace of purchases has depressed longer-term interest rates, keeping the 10-year Treasury yield around 75 basis points or lower over the last month or so.
Chatter is building over whether or not the Fed could pursue a more aggressive policy to pin down longer-term yields and keep borrowing costs low. Through a strategy called yield curve control, the Fed could commit to purchasing Treasuries of a given maturity until yields reach a target level.
Fedspeak even before COVID-19 hinted at taking on a version of yield curve control now adopted by the Reserve Bank of Australia, where the central bank targets medium-term yields (such as a three-year bond). The strategy is a toned down version of the Bank of Japan’s yield curve control policy, which targets longer-term yields (10-year bonds).
Fed officials say policymakers would like a little more time to discuss the issue.
“Right now it's way too premature to think about things like yield curve control,” Philadelphia Fed President Patrick Harker told Yahoo Finance on April 17.
Analysts at UBS wrote April 22 that they expect the Fed to eventually adopt some yield curve control policy, but would not expect an announcement until June. Nomura and TD Securities similarly expect an announcement later in the year.
...and the Treasury
Powell could also provide more details on its many liquidity facilities opened in conjunction with the U.S. Treasury.
Through section 13(3) of the Federal Reserve Act, the central bank is allowed to operate as a lender of last resort as long as the U.S. Treasury gives the Fed the blessing to do so. Over the last few weeks, Powell and Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin have moved quickly to do exactly that, opening nine facilities backing municipal debt, Paycheck Protection Program loans, asset-backed securities, corporate debt, and money markets.
The Fed has been unveiling new facilities and updating existing ones on a rolling basis. On Monday, the Fed expanded the scope and duration of its municipal lending facility to purchase even longer-dated bonds from more cities and counties.
But many of those facilities are not live yet, and one major facility - the Main Street Lending Facility - still needs final touches. As planned, the Fed hopes to offer cheap loans to businesses that are too large to qualify for the government’s PPP loans but too small to tap capital markets for fundraising.
The Fed solicited comments on the MSLF’s design in mid-April, meaning that the Fed could still make changes like including nonprofits into the facility.
“The Chair should spend time explaining any potential technical adjustments or updates to their programs, perhaps including expansions to or adjustments in the muni or Main Street facilities that will improve their effectiveness,” Deutsche Bank wrote.
The Fed’s decision is expected at 2pm ET on Wednesday followed by a videoconference with Powell at 2:30pm ET.
Brian Cheung is a reporter covering the Fed, economics, and banking for Yahoo Finance. You can follow him on Twitter @bcheungz.
Fed extends municipal liquidity facility beyond largest cities
Fed considers throwing universities a lifeline as furloughs begin
Philadelphia Fed's Harker: U.S. economy could contract by 5% in 2020
Richmond Fed's Barkin: Unemployment rate could soar to high teens
A glossary of the Federal Reserve's full arsenal of 'bazookas'
Read the latest financial and business news from Yahoo Finance
Follow Yahoo Finance on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, Flipboard, SmartNews, LinkedIn, YouTube, and reddit.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance 
